Automated on-line monitoring of the TiO2-based photocatalytic degradation of dimethyl phthalate and diethyl phthalate†
Abstract
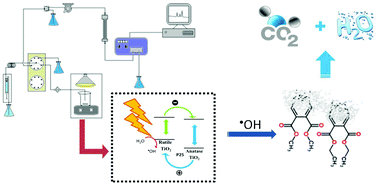
A fully automated on-line system for monitoring the TiO2-based photocatalytic degradation of dimethyl phthalate (DMP) and diethyl phthalate (DEP) using sequential injection analysis (SIA) coupled to liquid chromatography (LC) with UV detection was proposed. The effects of the type of catalyst (sol–gel, Degussa P25 and Hombikat), the amount of catalyst (0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 g L−1), and the solution pH (4, 7 and 10) were evaluated through a three-level fractional factorial design (FFD) to verify the influence of the factors on the response variable (degradation efficiency, %). As a result of FFD evaluation, the main factor that influences the process is the type of catalyst. Degradation percentages close to 100% under UV-vis radiation were reached using the two commercial TiO2 materials, which present mixed phases (anatase/rutile), Degussa P25 (82%/18%) and Hombikat (76%/24%). 60% degradation was obtained using the laboratory-made pure anatase crystalline TiO2 phase. The pH and amount of catalyst showed minimum significant effect on the degradation efficiencies of DMP and DEP. Greater degradation efficiency was achieved using Degussa P25 at pH 10 with 1.5 g L−1 catalyst dosage. Under these conditions, complete degradation and 92% mineralization were achieved after 300 min of reaction. Additionally, a drastic decrease in the concentration of BOD5 and COD was observed, which results in significant enhancement of their biodegradability obtaining a BOD5/COD index of 0.66 after the photocatalytic treatment. The main intermediate products found were dimethyl 4-hydroxyphthalate, 4-hydroxy-diethyl phthalate, phthalic acid and phthalic anhydride indicating that the photocatalytic degradation pathway involved the hydrolysis reaction of the aliphatic chain and hydroxylation of the aromatic ring, obtaining products with lower toxicity than the initial molecules.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Solar chemistry & photocatalysis: environmental applications – SPEA10


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...