Phenotype-based discovery of a HeLa-specific cytotoxic molecule that downregulates HPV-mediated signaling pathways via oxidative damage†
Abstract
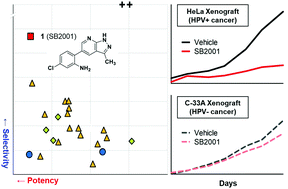
Selective bioactive compounds have emerged as major players in chemical biology for their potential in disrupting diverse biological pathways with minimal adverse effects. Using phenotypic screening, we identified an anti-cancer agent, SB2001, with a highly specific cytotoxicity toward HeLa human cervical cancer cells. The subsequent mechanistic study revealed that SB2001 induced apoptotic cell death through restoring p53 function and suppressed the human papillomavirus (HPV)-mediated oncoprotein signaling pathway via oxidative damage in HeLa cells. SB2001 also selectively induced HeLa-specific tumor regression without any adverse effects in an in vivo tumor xenograft model, demonstrating its potential as a promising chemical probe.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...