Rapid chelator-free radiolabeling of quantum dots for in vivo imaging†
Abstract
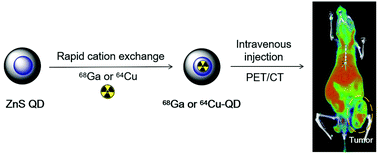
Most current nanoparticle-based PET tracers are radiolabeled through metal chelators conjugated on the nanoparticle surface. Metal chelation usually requires sophisticated optimization and may impact the physical or chemical properties of nanoparticles, which leads to the changes in their distribution and pharmacokinetics in vivo. A chelator-free radiolabeling approach is thus highly desirable. Here, we report that zinc sulfide (ZnS) quantum dots (QDs) can be rapidly radiolabeled with 68Ga or 64Cu through cation exchange without chelators. The radiolabeling was accomplished in times as short as 5 min at 37 °C in aqueous solution, yielding a high labeling efficiency and radiochemical purity for both isotopes. Surface functionalization with targeting peptides was also readily achieved to enable or enhance the cellular uptake of QDs. In vivo PET imaging showed that 64Cu-labeled QDs had a much higher tumor uptake (7.3% ID g−1) than 64Cu-DOTA in a murine cancer model. Overall, this study presents a QD-based platform to achieve convenient and chelator-free radiolabeling, and improve PET imaging of solid tumors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...