Nanocellulose/graphene oxide layered membranes: elucidating their behaviour during filtration of water and metal ions in real time†
Abstract
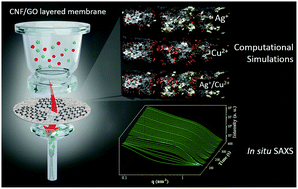
The deposition of a thin layer of graphene oxide onto cellulose nanofibril membranes, to form CNF–GO layered-composite membranes, dramatically enhances their wet-mechanical stability, water flux and capacity to adsorb water pollutants (P. Liu, C. Zhu and A. P. Mathew, J. Hazard. Mater., 2019, 371, 484–493). In this work, we studied in real time the behavior of these layered membranes during filtration of water and metal ion solutions by means of in situ SAXS and reactive molecular dynamics (ReaxFF) computational simulations. SAXS confirms that the GO layers limit the swelling and structural deformations of CNFs during filtration of aqueous solutions. Moreover, during filtration of metal ion solutions, the connection of the CNF–GO network becomes highly complex mass-fractal like, with an increment in the correlation length. In addition, after ion adsorption, the SAXS data revealed apparent formation of nanoparticles during the drying stage and particle size increase as a function of time during drying. The molecular dynamics simulations, on the other hand, provide a deep insight into the assembly of both components, as well as elucidating the motion of the metal ions that potentially lead to the formation of metal clusters during adsorption, confirming the synergistic behavior of GO and CNFs for water purification applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...