Carbon-loaded ultrafine fully crystalline phase palladium-based nanoalloy PdCoNi/C: facile synthesis and high activity for formic acid oxidation†
Abstract
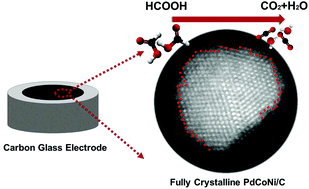
Recent studies have found surface engineering to be an effective strategy to improve the catalytic performance of noble-metal based catalysts. Herein, the successful synthesis of a fully crystalline PdCoNi alloy supported on carbon is reported. The as-synthesized catalyst has an ultrafine nanoparticle size distribution with low-coordination active sites distributed on the surface which was clearly captured by scanning transmission electron microscopy. The fully crystalline PdCoNi/C shows a significant enlarged electrochemical surface area (ECSA) and improved Pd-based mass activity and specific activity compared with bimetallic PdCo/C, PdNi/C and partly crystalline PdCoNi/C. An enhancement of the formic acid oxidation reaction activity can be explained by: (1) ultrafine size distribution from the greatly enlarged ECSA; (2) enhancement of the synergistic effect of the ternary PdCoNi alloy; (3) easier formation of a possible Pd intermediate state, PdHx, due to the regular atom arrangement being fully crystalline. This approach provides a strategy to design noble-metal-based catalysts for improved electrochemical performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...