Light-induced reversible hydrophobization of cationic gold nanoparticles via electrostatic adsorption of a photoacid†
Abstract
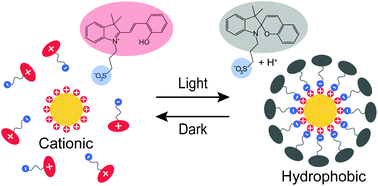
The ability to switch the hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of nanoparticles promises great potential for applications. Here we report a generic approach that allows hydrophobization of cationic surfaces by light-induced photoacid switching from the unbound zwitterionic form to the electrostatically bound anionic form. Importantly, this allows reversible assembly and disassembly of cationic AuNPs, with disassembly kinetics controlled by temperature. The AuNPs can be repeatedly transferred between aqueous and non-polar solvents using light, showing potential in purification processes. In the macroscopic scale, nontrivially, light triggers the in situ hydrophobization of a flat cationized gold surface. The current approach is generic and opens up a new way to control the surface properties and self-assembly of nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...