Exploring antiaromaticity in single-molecule junctions formed from biphenylene derivatives†
Abstract
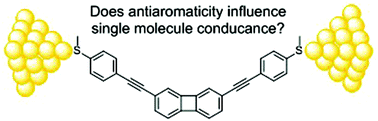
We report the synthesis of a series of oligophenylene-ethynylene (OPE) derivatives with biphenylene core units, designed to assess the effects of biphenylene antiaromaticity on charge transport in molecular junctions. Analogues with naphthalene, anthracene, fluorene and biphenyl cores are studied for comparison. The molecules are terminated with pyridyl or methylthio units. Single-molecule conductance data were obtained using the mechanically controllable break junction (MCBJ) technique. It is found that when electrons pass from one electrode to the other via a phenylene ring, the electrical conductance is almost independent of the nature of the pendant π-systems attached to the phenylene ring and is rather insensitive to antiaromaticity. When electrons pass through the cyclobutadiene core of the biphenylene unit, transport is sensitive to the presence of the relatively weak single bonds connecting the two phenylene rings of biphenylene, which arise from partial antiaromaticity within the cyclobutadiene core. This leads to a negligible difference in the molecular conductance compared to the fluorene or biphenyl analogues which have standard single bonds. This ability to tune the conductance of molecular cores has no analogue in junctions formed from artificial quantum dots and reflects the quantum nature of electron transport in molecular junctions, even at room temperature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...