Tuning the catalytic activity and selectivity of water-soluble bimetallic RuPt nanoparticles by modifying their surface metal distribution†
Abstract
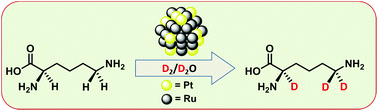
Bimetallic ruthenium–platinum nanoparticles (RuPt NPs) of different surface distributions and stabilized by using a sulfonated N-heterocyclic carbene ligand (1-(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-3-(3-potassium sulfonatopropyl)-imidazol-2-ylidene) were prepared from Ru(COD)(COT) (COD = cyclooctadiene and COT = cyclooctatriene), and platinum precursors having various decomposition rates (Pt(NBE)3, NBE = norbornene, Pt(CH3)2(COD) and Pt2(DBA)3, DBA = dibenzylideneacetone). Structural and surface studies by FT-IR and solid-state MAS NMR, using carbon monoxide as a probe molecule, revealed the presence of different structures and surface compositions for different nanoparticles of similar sizes, which principally depend on the decomposition rate of the organometallic precursors used during the synthesis. Specifically, the slower the decomposition rate of the platinum precursor, the higher the number of Pt atoms at the NP surface. The different bimetallic RuPt NPs, as well as their monometallic equivalents (Pt and Ru NPs), were used in isotopic H/D exchange through C–H activation on L-lysine. Interestingly, the activity and selectivity of the direct C–H deuteration were dependent on the NP surface composition at the α position but not on that at the ε position. Chemical shift perturbation (CSP) experiments revealed that the difference in reactivity at the α position is due to a Pt–carboxylate interaction, which hinders the H/D exchange.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...