Controlling photon antibunching from 1D emitters using optical antennas†
Abstract
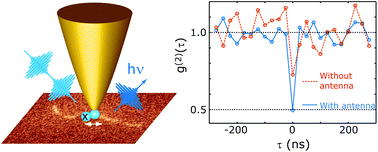
Single-photon emission is a hallmark of atom-like 0D quantum emitters, such as luminescent semiconductor nanocrystals, nitrogen vacancies in diamond and organic dye molecules. In higher dimensional nanostructures, on the other hand, multiple spatially separated electronic excitations may exist giving rise to more than one emitted photon at a time. We show that optical nanoantennas can be used to control the photon emission statistic of 1D nanostructures and to convert them into single-photon sources. Antenna-control exploits spatially confined near-field enhanced absorption and emission rates resulting in locally increased annihilation of mobile excitons and radiative recombination. As proof of concept, we experimentally demonstrate the improvement of the degree of antibunching in the photoluminescence of single carbon nanotubes using a metal tip at room temperature. Our results indicate that, in addition to improving the performance of single photon sources, optical antennas have the potential to open up a broad range of materials for quantum information technology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...