The release and detection of copper ions from ultrasmall theranostic Cu2−xSe nanoparticles†
Abstract
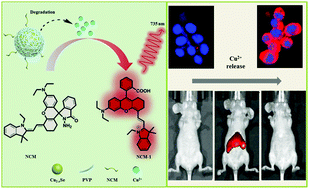
Nanoscale copper chalcogenides have been widely used in nanomedicine, however, their pharmacokinetics, degradation, and biological effects of released copper ions are usually overlooked, which are crucial for their future clinical translation. Herein, we report the in vitro and in vivo release of copper ions from polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) functionalized ultrasmall copper selenide (Cu2−xSe) theranostic nanoparticles. We synthesized a Cu2+-specific fluorescent probe (NCM), which can quickly and specifically react with copper ions to exhibit very strong near infrared fluorescence. The in vitro study shows that copper ions can be slowly released from Cu2−xSe nanoparticles in aqueous solution with the progress of their oxidation. The release of copper ions from Cu2−xSe nanoparticles in RAW 264.7 murine macrophages is very fast, evidenced by the gradual increase of fluorescence intensity and the diffusion of fluorescence from cytoplasm into nuclei. We also demonstrate the distribution, degradation, and the metabolism of ultrasmall Cu2−xSe nanoparticles by the in vivo fluorescence imaging, the blood routine test, blood biochemistry and histology analysis, and the characterization of copper transport and binding proteins. The results show that ultrasmall Cu2−xSe nanoparticles were mainly eliminated through feces and urine from the body within 72 h after intravenous injection, and the released copper ions did not cause severe toxicity. Our research highlights the great potential of copper chalcogenide nanoparticles in nanomedicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...