Enzyme-catalysed biodegradation of carbon dots follows sequential oxidation in a time dependent manner†
Abstract
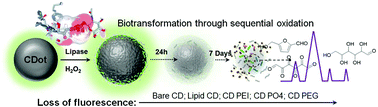
Carbon dots (CDs) have recently garnered significant attention owing to their excellent luminescence properties, thereby demonstrating a variety of applications in in vitro and in vivo imaging. Understanding the long-term metabolic fate of these agents in a biological environment is the focus of this work. Here we show that the CDs undergo peroxide catalysed degradation in the presence of lipase. Our results indicate that differently charged CD species exhibit unique degradation kinetics upon being subjected to enzyme oxidation. Furthermore, this decomposition correlates with the relative accessibility of the enzymatic molecule. Using multiple physico-chemical characterization studies and molecular modelling, we confirmed the interaction of passivating surface abundant molecules with the enzyme. Finally, we have identified hydroxymethyl furfural as a metabolic by-product of the CDs used here. Our results indicate the possibility and a likely mechanism for complete CD degradation in living systems that can pave the way for a variety of biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...