Insights into supramolecular-interaction-regulated piezochromic carbonized polymer dots†
Abstract
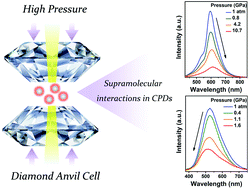
The photoluminescence (PL) mechanism plays a significant role in the study of carbonized polymer dots (CPDs). The supramolecular interaction exists in most materials, which offers innate methods to regulate the optical and physical properties. However, insights into the tunable red- and blue-shifted PL peaks of CPDs by the supramolecular interaction still remain elusive. Herein, the supramolecular interaction-triggered fluorescence change of CPDs is reported by the investigation of the piezochromic behaviors. The π-conjugated system and the hydroxy group are both critical to manipulate the PL of CPDs under high pressure. The π–π stacking of the π-conjugated system was enhanced with increasing pressure, which induces the red-shifting of PL peaks, while the hydroxyl-related hydrogen bond formation eventually causes a blue-shift. In addition, their chemical stability, low toxicity, and the tunable PL properties of CPDs by supramolecular interaction under high pressure would deepen the understanding of the fluorescence mechanism of CPDs, inspiring extensive application prospects in sensing and light-emitting diodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...