Preparation of Au@Ag core–shell nanoparticle decorated silicon nanowires for bacterial capture and sensing combined with laser induced breakdown spectroscopy and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
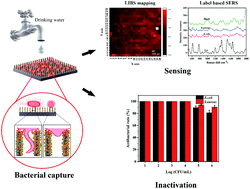
Three-dimensional nano-biointerfaces, emerging as significant cell-guiding platforms, have attracted great attention. Nevertheless, complicated chemical modifications and instability of bio-ligands limit their widespread application. In this study, a novel biointerface, based on silicon nanowires (SiNWs) array, was prepared for bacterial capture and sensing. Vertically aligned SiNWs were fabricated via metal assisted chemical etching and decorated with uniform Au@Ag core–shell nanoparticles (Au@Ag NPs). These deposited Au@Ag NPs formed multi-scale topographic structures with nanowires, which provided effective attachment sites for bacterial adhesins. In addition, the Au cores of Au@Ag NPs enhanced the activity of the surface silver atoms and promoted the binding of Au@Ag NPs to bacteria. Thus, the Au@Ag NPs decorated SiNWs (SiNWs-Au@Ag) substrate exhibited high capture capacity for bacteria in drinking water (8.6 and 5.5 × 106 cells per cm2 for E. coli and S. aureus in 40 min, respectively) via physical and chemical effects. Bacteria in drinking water can be sensitively detected by using a combination of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and label based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) techniques. Due to the antibacterial activity of Au@Ag NPs and the physical stress exerted on SiNWs, the prepared biointerface also showed high antibacterial rates towards both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria strains. With these excellent properties, the flexible sensing platform might open a new avenue for the prevention and control of microbial hazards in water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...