IGF signalling and endocytosis in the human villous placenta in early pregnancy as revealed by comparing quantum dot conjugates with a soluble ligand†
Abstract
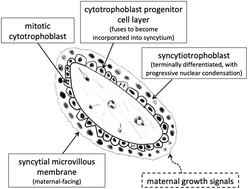
A complex combination of trafficking and signalling occurs at the surface of the placenta. The system delivers maternal nutrients to the fetus and facilitates gaseous exchange, whilst mediating signal transduction to support and stimulate the growth of the placenta itself. IGF-I is acknowledged as a maternally-derived ligand important in the regulation of placental growth. Here we show that quantum dots bearing IGF can stimulate IGF receptor (IGF1R) phosphorylation in the syncytio- (maternal-facing) and cyto- (fetal-facing) trophoblast bilayer that forms the outer boundary of the placenta, in a distribution similar to the one resulting from exposure to a soluble ligand. The conjugates are internalised by a clathrin-dependent pathway and delivered to a syncytioplasmic compartment that differs from conventional late endosomes and lysosomes. Two discrete downstream responses are evident in different cellular compartments: phosphorylation of P70S6K in the non-proliferative syncytiotrophoblast and of AKT in the cytotrophoblast. Co-conjugation of IGF-quantum dots with an RGD-containing ligand permits penetration beyond the syncytium, into the cytoplasm of the underlying cytotrophoblast. These data reveal the existence of a trans-syncytial pathway that allows maternal mitotic signals to penetrate to the inner progenitor cells, which must proliferate to support placental and consequently fetal growth.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...