Breathing new life into old antibiotics: overcoming antibacterial resistance by antibiotic-loaded nanogel carriers with cationic surface functionality†
Abstract
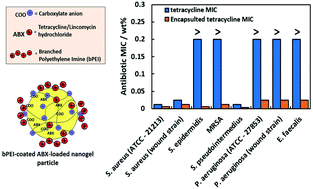
Multidrug-resistant pathogens are prevalent in chronic wounds. There is an urgent need to develop novel antimicrobials and formulation strategies that can overcome antibiotic resistance and provide a safe alternative to traditional antibiotics. This work aimed to develop a novel nanocarrier for two cationic antibiotics, tetracycline hydrochloride and lincomycin hydrochloride which can potentially overcome antibiotic resistance. In this study, we report the use of surface functionalised polyacrylic copolymer nanogels as carriers for cationic antibiotics. These nanogels can encapsulate small cationic antimicrobial molecules and act as a drug delivery system. They were further functionalised with a biocompatible cationic polyelectrolyte, bPEI, to increase their affinity towards the negatively charged bacterial cell walls. These bPEI-coated nanocarrier-encapsulated antibiotics were assessed against a range of wound isolated pathogens, which had been shown through antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) to be resistant to tetracycline and lincomycin. Our data reveal that bPEI-coated nanogels with encapsulated tetracycline or lincomycin displayed increased antimicrobial performance against selected wound-derived bacteria, including strains highly resistant to the free antibiotic in solution. Additionally, our nanocarrier-based antibiotics showed no detectable cytotoxic effect against human keratinocytes. We attribute the increase in the antimicrobial activity of the cationically functionalised antibiotic-loaded nanogel carriers to specific electrostatic adhesion to the microbial cell wall delivering a higher local antibiotic concentration, confirmed by scanning electron microscopy. Such a nanotechnology based approach may enhance the effectiveness of a wide variety of existing antibiotics, offering a potentially new mechanism to overcome antibiotic resistance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...