Ultrathin Ta2O5 electron-selective contacts for high efficiency InP solar cells†
Abstract
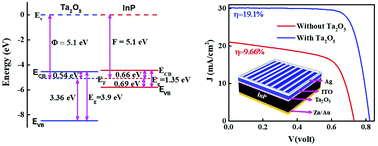
Heterojunction solar cells with transition-metal–oxide-based carrier-selective contacts have been gaining considerable research interest owing to their amenability to low-cost fabrication methods and elimination of parasitic absorption and complex semiconductor doping process. In this work, we propose tantalum oxide (Ta2O5) as a novel electron-selective contact layer for photo-generated carrier separation in InP solar cells. We confirm the electron-selective properties of Ta2O5 by investigating band energetics at the InP–Ta2O5 interface using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Time-resolved photoluminescence and power dependent photoluminescence reveal that the Ta2O5 inter-layer also mitigates parasitic recombination at the InP/transparent conducting oxide interface. With an 8 nm Ta2O5 layer deposited using an atomic layer deposition (ALD) system, we demonstrate a planar InP solar cell with an open circuit voltage, Voc, of 822 mV, a short circuit current density, Jsc, of 30.1 mA cm−2, and a fill factor of 0.77, resulting in an overall device efficiency of 19.1%. The Voc is the highest reported value to date for an InP heterojunction solar cells with carrier-selective contacts. The proposed Ta2O5 material may be of interest not only for other solar cell architectures including perovskite cells and organic solar cells, but also across a wide range of optoelectronics applications including solid state emitting devices, photonic crystals, planar light wave circuits etc.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...