Enhanced radiosensitization of ternary Cu3BiSe3 nanoparticles by photo-induced hyperthermia in the second near-infrared biological window†
Abstract
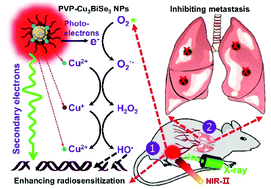
The development of a new multifunctional nanomedicine capable of enhancing radiosensitization by photo-induced hyperthermia for the inhibition of cancer growth and metastasis is highly required for efficient treatment of cancer cells. Compared to the first near-infrared (NIR) window, the second NIR window light could provide a maximum penetration depth as well as minimizing autofluorescence due to its low scattering and energy absorption. Here, we report a new versatile theranostic agent based on ternary Cu3BiSe3 nanoparticles (NPs) modified by poly(vinylpyrollidone) (PVP-Cu3BiSe3). Benefiting from their preferable X-ray attenuation ability and strong NIR absorbance in the second NIR biological window, PVP-Cu3BiSe3 NPs can not only deposit more radiation doses to destroy the cancer cells, but also conduct the optical energy into hyperthermia for thermal eradication of tumor tissues and the improvement of the tumor oxygenation to overcome the hypoxia-associated radio-resistance of tumors. According to both in vitro and in vivo results, exposure to an X-ray plus 1064 nm laser completely kills cancer cells and even inhibits tumor metastasis, displaying no warning signs of a relapse. On the other hand, PVP-Cu3BiSe3 NPs can be used as a multi-model imaging agent for X-ray computer tomography (CT) and photoacoustic tomography (PAT) imaging. These demonstrate the potential of PVP-Cu3BiSe3 NPs in multimodal imaging-guided synergetic radiophotothermal therapy of deep-seated tumors and effective inhibition of their metastasis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...