A reliable procedure for the preparation of graphene-boron nitride superlattices as large area (cm × cm) films on arbitrary substrates or powders (gram scale) and unexpected electrocatalytic properties†
Abstract
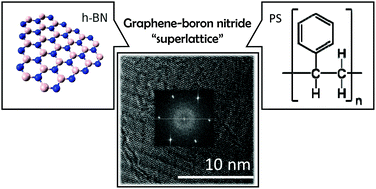
Herein, a reliable procedure for the preparation of graphene-boron nitride superlattices, either as films or powders, consisting of the pyrolysis at 900 °C of polystyrene embedded pre-formed boron nitride single sheets is reported. The procedure can serve to prepare large area films (cm × cm) of this superlattice on quartz, copper foil and ceramics. Selected area electron diffraction patterns at every location on the films show the occurrence of the graphene-boron nitride superlattice all over the film. The procedure can also be applied to the preparation of powdered samples on a gram scale. Comparison with other materials indicates that the superlattice appears spontaneously as the growing graphene sheets develop, due to the templating effect of pre-existing boron nitride single sheets. Since the characteristic boron nitride emission in the visible region is completely quenched in the superlattice configuration, it is proposed that fluorescence microscopy can be used as a routine technique to determine the occurrence of superlattice in large area films. Electrodes of this material show an unforeseen catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction and exhibit a decrease of the heterojunction-electrolyte interphase electrical resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...