One-pot synthesis of PtIn/3D-GNs composites with high alloying degree for electro-photo synergistic catalysis
Abstract
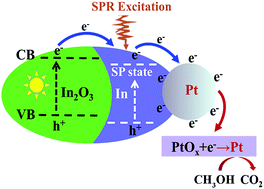
In this work, a one-pot solid phase reaction was used to synthesize PtIn/3D-GNs composites with different alloying degrees. The as-synthesized composites were characterized by using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results indicate that PtIn alloy was formed in the PtIn/3D-GNs composites. However, In(0) content in the composites (denoted as PtIn/3D-GNs (O)) when In2O3 was used as a precursor of In is almost twice as much as that in the composites (denoted as PtIn/3D-GNs (S)) using In(NO3)3 as a precursor of In, which indicates the higher Pt–In alloying degree in PtIn/3D-GNs (O). Electrochemical tests show that PtIn/3D-GNs composites exhibit superior electrocatalytic activity, better stability and enhanced antipoisoning ability toward methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) in comparison with Pt/3D-GNs and the commercial Pt/C. Interestingly, the synergistic effect between the charge separation of In2O3 and the SPR excitation of In(0) under light irradiation contributes to their good electro-photocatalytic performance under simulated sunlight irradiation. Especially, the higher Pt–In alloying degree in PtIn/3D-GNs (O) contributes to its better conductivity, which is responsible for its more efficient electro-photocatalytic properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...