Reaction kinetic properties of 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene: a DFTB study of thermal decomposition†
Abstract
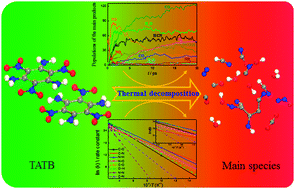
The thermal decomposition of 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TATB) is studied using a quantum-based molecular dynamics (MD) method at several temperatures, to uncover its fundamental reaction mechanism and kinetic properties. The primary decomposition pathways, key intermediate products and their population evolutions are systematically investigated. For the first time, we uncover four sequential reaction stages during the thermal dissociation of TATB: (1) C–NO2 bond cleavage and amino dehydrogenation; (2) hydrogen transfer to nitro or NO2, with further conversion to NO and H2O; (3) carbon oxidation and molecular ring deep fission to generate CO and small –CN fragments; (4) final formation of gaseous N2 and CO2. The fission and formation rate constants and reaction energy barriers of the main chemical bonds are obtained by exploring the kinetic process. We confirm that C–NH2 bond breaking is the rate-controlling step for carbon oxidation, while N–N bond formation is the rate-controlling step for N2 generation. Besides, we obtain the global exothermic reaction rate and reaction heat based on an analysis of the changes in potential energy. The results not only give a deep insight into the chemical performance of TATB, but also provide prerequisite parameters for improving the macroscopic physical models for explosive reactivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...