Selective detection and removal of mercury ions by dual-functionalized metal–organic frameworks: design-for-purpose†
Abstract
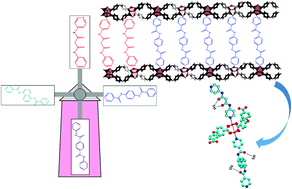
In this study, through introducing a new functional group into the structure, the performance and efficiency of MOFs as a sensor for heavy metal cations have been improved. It was observed that the N1,N3-di(pyridine-4-yl) malonamide ligand (–NH–CO–CH2–CO–NH–)(S), one of the pillar linkers, has not directly entered into the structure of the synthesized MOFs. To solve this issue, three new structures based on copper metal–organic frameworks and amide-functionalized pillar ligands (–NH–CO–), TMU-46, 47 and 48 have been synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. An exciting aspect of the acylamide pillar ligands is their efficient detection ability of Hg2+ (mercury ion) in the presence of other heavy metal cations such as Cd2+ (cadmium), Cu2+ (copper), and Cr3+ (chromium). Due to their chelating effect on heavy metal cations, we hypothesized that decoration of the MOF wall with both malonamide and acylamide struts would promote their Lewis basic properties, and improve the removal capacity of heavy metal ions. A new linker, containing suitable functional group malonamide (S) to enhance Hg2+ cation sensing, was successfully exchanged and the produced material was labeled TMU-46S, TMU-47S and TMU-48S. Designing dual-functionalized MOFs is our “design-for-purpose” approach for the decoration of MOF walls by suitable functional groups resulting in high removal capacity and sensitivity of heavy metal ions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a mixed amide-malonamide based MOF which provides a proper coordination site to coordinate strongly to Hg2+ ions, along with 714 mg g−1 maximum adsorption capacity and 186 087 M−1Ksv. Generally, we attributed the impressive Hg2+ sensing of TMU-48S to synergistic effects of both hydrophilic chelating malonamide and acylamide functional groups. Hence, the results represent an effective strategy in designing and developing multi-functional MOF-based materials and their application in removal processes and environmental protection efforts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...