Reactivities of MeO-substituted PBN-type nitrones†
Abstract
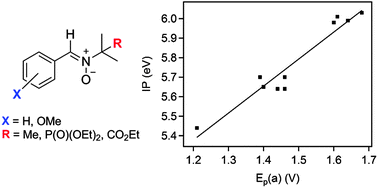
In this work, α-phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone (PBN), N-benzylidene-1-diethoxyphosphoryl-1-methylethylamine N-oxide (PPN) and N-benzylidene-1-ethoxycarbonyl-1-methylethylamine N-oxide (EPPN) derivatives bearing methoxy groups (MeO-) on the phenyl ring were synthesized. Their electrochemical properties were studied by cyclic voltammetry and the results showed that the position and the number of methoxy substituents influence the redox potential of the nitronyl group. The spin-trapping ability of the derivatives was next investigated by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy for the hydroxymethyl radical (˙CH2OH). The ortho, meta and para mono-substituted-PBN derivatives exhibited similar trapping rates to the parent PBN while surprisingly, nitrones with two MeO-substituents on the ortho-position failed to trap ˙CH2OH. The trapping rates of the parent compounds were ranked as follows: PPN > EPPN > PBN, indicating that the presence of diethoxyphosphoryl and ethoxycarbonyl electron withdrawing groups on the N-tert-butyl group significantly enhanced the reactivity towards hydroxymethyl radicals. The effect of the substitutions on the atomic partial charges of the nitronyl-moiety and on the ionization potential was computationally rationalized and showed a strong correlation between the ionization potential and the experimentally measured oxidation potential.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...