A comparative study on NHC-functionalized ternary Se/Te–Fe–Cu compounds: synthesis, catalysis, and the effect of chalcogens†
Abstract
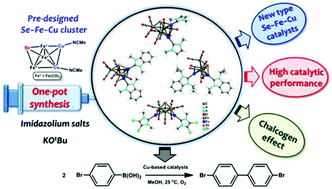
A novel family of N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-incorporated Se–Fe–Cu compounds, bis-1,3-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene (bis-Me2-imy)-containing compound [(μ4-Se)Fe3(CO)9{Cu(Me2-imy)}2] (2), bis-N-methyl- or bis-N-isopropyl-substituted benzimidazol-2-ylidene (bis-Me2-bimy or bis-iPr2-bimy)-incorporated compounds [(μ4-Se)Fe3(CO)9{Cu(Me2-bimy)}2] (3) or [(μ4-Se)Fe3(CO)9{Cu(iPr2-bimy)}2] (4), and a bis-1,3-dimethyl-4,5-dichloroimidazol-2-ylidene (bis-Me2-Cl2-imy)-containing compound [(μ3-Se)Fe3(CO)9{Cu(Me2-Cl2-imy)}2] (5), were synthesized in moderate yields in facile one-pot reactions of the ternary pre-designed compound [(μ3-Se)Fe3(CO)9{Cu(MeCN)}2] (1) with the corresponding imidazolium salts and KOtBu in THF in an ice-water bath. Single-crystal X-ray analyses revealed that the Me2-imy compound 2 or the Me2-bimy compound 3 each exhibited a trigonal bipyramidal SeFe3(CO)9Cu geometry with an Fe2Cu plane further capped by a Cu(Me2-imy) or Cu(Me2-bimy) fragment, respectively, with one long Cu–Cu covalent bond. In addition, compound 4 also comprised a trigonal bipyramidal SeFe3(CO)9Cu core structure, but the second Cu(iPr2-bimy) group bridged the equatorial Fe–Fe edge with two unbonded Cu atoms, due to the presence of a sterically bulky iPr2-bimy fragment. On the other hand, the strong electron-withdrawing chloro-containing NHC compound 5 showed a comparatively open tetrahedral SeFe3(CO)9 metal core, where two Fe–Fe edges each were further bridged by a Cu(Me2-Cl2-imy) fragment. Due to the nonclassical C–H⋯O(carbonyl) hydrogen bonds between the CO groups of the SeFe3(CO)9Cu2 core and CH moieties of the neighboring NHC ligands, both compounds 2 and 3 comprised a one-dimensional network, while compounds 4 and 5 each were made up of a two-dimensional framework in the solid state, which efficiently enhanced the stability of these Se–Fe–Cu NHC compounds. Importantly, all of these synthesized Se–Fe–Cu NHC compounds 2–5 had pronounced catalytic activities for the homocoupling of arylboronic acids with high catalytic yields. Finally, these Se-containing Fe–Cu NHC compounds further represented excellent models for studying chalcogen effects in comparison to their Te analogs, as demonstrated by their catalytic performances and electrochemical behaviors, and by DFT calculations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Selenium & Tellurium chemistry at the beginning of the 3rd millennium: a celebration of ICCST

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...