Ligand-free Cu(ii)-catalyzed aerobic etherification of aryl halides with silanes: an experimental and theoretical approach†
Abstract
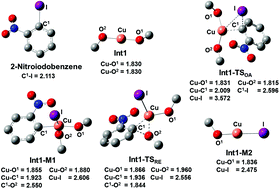
Owing to their wide occurrence in nature and immense applications in various fields, the synthesis of aryl alkyl ethers has remained a focus of interest. In contrast to the conventional/traditional methods of etherification, herein, we have reported a more efficient method, which is better yielding and more general in application. The etherification of aryl halides by alkoxy/phenoxy silanes was catalyzed by copper acetate in the presence of cesium carbonate and oxygen in DMF at 145 °C. All the as-synthesized compounds were characterized via the 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopic techniques. Density functional theory calculations using the B3LYP functional were performed to elucidate the reaction mechanism. The C–O coupling reaction between 2-nitroiodobenzene and tetramethoxysilane was used as a model reaction. The activation energy barriers for the generation of catalytic species (31.6 kcal mol−1) and the σ-bond metathesis (16.0 kcal mol−1), oxidative addition/reductive elimination (20.3 kcal mol−1), halogen atom transfer (19.2 kcal mol−1) and single electron transfer (SET) (29.5 kcal mol−1) mechanisms for the C–O coupling reaction were calculated. Calculations for the key reaction steps were repeated with the B3PW91, PBEH1PBE, wB97XD, CAM-B3LYP and mPW1LYP functionals. The formation of catalytic species via a single electron transfer reaction between tetramethoxysilane and copper acetate, formation of methoxy radicals and methoxylation of copper showed an overall energy barrier of 31.6 kcal mol−1, and therefore is the rate determining step.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...