Annulated bacteriochlorins for near-infrared photophysical studies†
Abstract
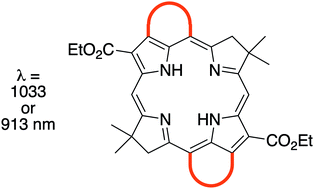
Molecules with strong absorption in the near-infrared (NIR) spectral region are of interest for a variety of applications in the photosciences. Nature's NIR absorbers are bacteriochlorophylls, which contain a tetrahydroporphyrin chromophore accentuated by attached auxochromes, including a β,meso-bridging isocyclic ring. Modification of the isocyclic ring has provided a convenient means of wavelength tuning. In other tetrapyrroles, annulation at the β,meso-, β,β-, and β-meso-β-positions also has enabled wavelength tuning. Here, synthetic bacteriochlorins bearing a gem-dimethyl group in each pyrroline ring have provided the foundation for studies of annulation. Seven new free base bacteriochlorins have been prepared and seven others have been elaborated therefrom. Six distinct routes known among porphyrins were explored. Ultimately, annulation of phenaleno or benzo groups at the β,meso-sites (i.e., spanning the 3,5- and 13,15-positions) of bacteriochlorins was achieved by a new route that entails two successive Pd-mediated coupling reactions of a dibromobacteriochlorin with a bromoarylboronic acid. The corresponding Phen-BC or Benz-BC absorbs at 913 or 1033 nm, respectively. Examination by time-resolved spectroscopy revealed an excited-state lifetime of 150 ps or 7 ps, with commensurably low fluorescence quantum yield (Φf) values estimated to be ∼0.004 or 3 × 10−5, respectively. The origin of the short excited-state lifetimes due to β,meso-annulation is unknown, but is not simply a consequence of the energy-gap law for non-radiative decay.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...