A colorimetric and “off–on” fluorescent Pd2+ chemosensor based on a rhodamine-ampyrone conjugate: synthesis, experimental and theoretical studies along with in vitro applications†
Abstract
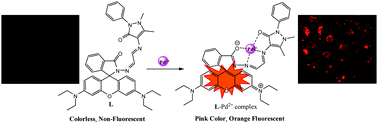
We successfully designed and developed a rhodamine based “turn-on” chemosensor L for the detection of Pd2+ ions down to 1.19 × 10−5 M (11.9 μM). In organo-aqueous solution, probe L displayed highly selective and sensitive colorimetric and fluorescence responses toward Pd2+ based on the ring-opening mechanism of the rhodamine spirolactam ring upon complexation with Pd2+. In the presence of Pd2+ ions, probe L formed an L–Pd2+ complex in 1 : 1 stoichiometry which was confirmed by the Job plot and mass spectroscopy. Moreover, we performed DFT (density functional theory) studies to identify the coordination characteristics and binding nature of L and the L–Pd2+ complex. In addition, cell imaging experiments revealed that probe L was able to permeate cells, and able to image Pd2+ in living cells.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...