Enhanced optical temperature sensing and upconversion emissions based on the Mn2+ codoped NaGdF4:Yb3+,Ho3+ nanophosphor
Abstract
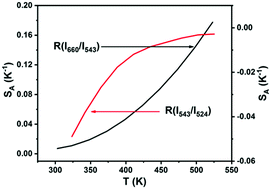
In this study, to explore new phosphors for temperature sensing with high detection sensitivity, Yb3+/Ho3+/Mn2+ doped hexagonal NaGdF4 nanoparticles were designed. These nanoparticles were synthesized by a hydrothermal method while using oleic acid as both a stabilizing and a chelating agent. The morphology and the crystal size of the upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) were effectively controlled through the addition of Mn2+ dopant contents into the NaGdF4:Yb/Ho system. Moreover, an enhancement in the overall upconversion luminescence (UCL) spectra of Mn2+ doped UCNPs for the NaGdF4 host compared to Mn2+ free UCNPs was observed, which resulted from the close back-energy transfer between Ho3+ and Mn2+ ions (5F3 and 5F4,5S2 (Ho3+) → 4T1 (Mn2+) → 5F5 (Ho3+)). The calculated color coordinates displayed that with the increase of pump power densities, the tendency of orange-red output turned toward the green region, revealing that the UC emission can be fine-tuned in a wide range of pump power densities. Importantly, the temperature sensitivity of NaGdF4:Yb/Ho doped with Mn2+ based on thermally coupled levels (5F4 and 5S2) and non-thermally coupled levels (5F5 and 5S2) of Ho3+ was significantly enhanced compared to other jobs. The maximum sensitivity reached 0.0051 K−1 at 303 K and 0.199 K−1 at 523 K, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...