Cascade aldol condensation of an aldehyde via the aerobic oxidation of ethanol over an Au/NiO composite
Abstract
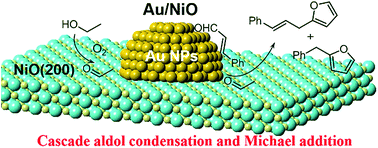
Synthesis of liquid biofuels (C11–C13) from cellulosic ethanol is regarded as a promising and versatile protocol. In this study, oxide-supported nanogold catalysts exhibit good catalytic performance in ethanol conversion with cinnamaldehyde and finally give rise to the C11–C13 hydrocarbon. High selectivity (70%) for C11–C13 hydrocarbons is achieved over Au/NiO via a one-pot cascade reaction, viz. cross-aldol condensations in the presence of oxygen and base (K2CO3) and then full hydrodeoxygenation with hydrogen gas. EtOH-TPD and TGA analyses show that the ethanol is activated to acetaldehyde (CH3CHO*) over the surface oxygen vacancies of the NiO support. The CH3CHO* then reacts with cinnamaldehyde at the interfacial perimeter of the Au/NiO composite during the cascade reactions, as evidenced by comparison of the catalytic performance with that over another oxide-supported Au NP, chemo-adsorption investigations, and in situ infrared spectroscopy investigations. This work may provide new guidelines for designing efficient catalysts to convert bioethanol into biofuels with high energy density.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...