A MoS2–MWCNT based fluorometric nanosensor for exosome detection and quantification†
Abstract
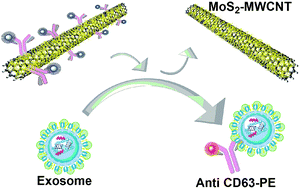
Circulating exosomes in body fluids are involved in many diseases and have important roles in pathophysiological processes. Specifically, they have emerged as a promising new class of biomarkers in cancer diagnosis and prognosis because of their high concentration and availability in a variety of biological fluids. The ability to quantitatively detect and characterize these nano-sized vesicles is crucial to make use of exosomes as a reliable biomarker for clinical applications. However, current methods are mostly technically challenging and time-consuming which prevents them from being adopted in clinical practice. In this work, we have developed a rapid sensitive platform for exosome detection and quantification by employing MoS2–multiwall carbon nanotubes as a fluorescence quenching material. This exosome biosensor shows a sensitive and selective biomarker detection. Using this MoS2–MWCNT based fluorometric nanosensor to analyze exosomes derived from MCF-7 breast cancer cells, we found that CD63 expression could be measured based on the retrieved fluorescence of the fluorophore with a good linear response range of 0–15% v/v. In addition, this nanosensing technique is able to quantify exosomes with different surface biomarker expressions and has revealed that exosomes secreted from MCF-7 breast cancer cells have a higher CD24 expression compared to CD63 and CD81.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...