Enabling the electrocatalytic fixation of N2 to NH3 by C-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under ambient conditions†
Abstract
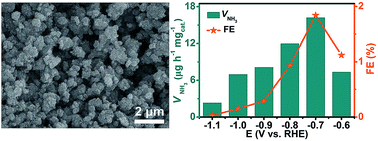
The conventional Haber–Bosch process for industrial NH3 production from N2 and H2 is highly energy-intensive with a large amount of CO2 emissions and finding a more suitable method for NH3 synthesis under mild conditions is a very attractive topic. The electrocatalytic N2 reduction reaction (NRR) offers us an environmentally benign and sustainable route. In this communication, we report that C-doped TiO2 nanoparticles act as an efficient electrocatalyst for the NRR with excellent selectivity. In 0.1 M Na2SO4, it achieves an NH3 yield of 16.22 μg h−1 mgcat.−1 and a faradaic efficiency of 1.84% at −0.7 V vs. the reversible hydrogen electrode. Furthermore, this catalyst also shows good stability during electrolysis and recycling tests.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...