Copper(ii) complexes with alloferon analogues containing phenylalanine H6F and H12F stability and biological activity lower stabilization of complexes compared to analogues containing tryptophan†
Abstract
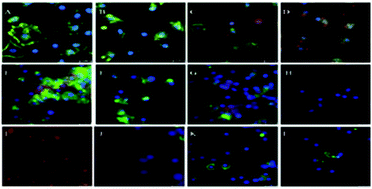
Copper(II) complex formation processes between alloferon 1 (Allo1) (H1 GVSGH6 GQH9 GVH12G) analogues where the phenylalanine residue is introduced in the place of His residue H6F and H12F have been studied by potentiometric, UV-visible, CD and EPR spectroscopic, and MS methods. For the phenylalanine analogues of alloferon 1, complex speciation has been obtained for a 1 : 1, 2 : 1 and 3 : 1 metal-to-ligand molar ratio. At physiological pH and in 1 : 1 metal-to-ligand molar ratio the phenylalanine analogues of alloferon 1 form a CuL complex similar to that of alanine analogues with the 4N{NH2,N1Im,2NIm} coordination mode. The stability of the complexes of the phenylalanine analogues is higher in comparison to those of alanine analogues, but lower in comparison to those containing tryptophan. Injection of Allo12F into insects induced prominent apoptotic changes in all hemocytes. The presence of apoptotic bodies only in the insect hemolymph testifies to the fact that Allo12F is an extremely pro-apoptotic peptide.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...