Gene expression profile-based drug screen identifies SAHA as a novel treatment for NAFLD†
Abstract
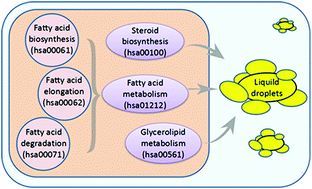
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease worldwide. Being part of the metabolic syndrome, NAFLD is characterized by the deposition of triglycerides (TGs) as lipid droplets in the cytoplasm of hepatic cells. Recently, the rapid development of high-throughput genome analysis technologies provided opportunities to screen for new drugs for NAFLD. In this study, we screened for potential drugs based on the gene expression profiles of 73 compounds and identified histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors as a novel treatment for the accumulation of lipids in hepatocytes. In the subsequent analysis and experiments, we discovered that SAHA inhibited the fatty acid and lipid metabolism pathways in hepatic cells and induced a significant deficiency of lipid accumulation in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells. Furthermore, SAHA inhibited lipid synthesis in hepatic cells by directly suppressing the expression of DGAT2. Hence, our study provides a novel method to screen for effective drugs for liver diseases and identifies SAHA as a potent treatment for NAFLD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...