Benzoazacrown compound: a highly effective chelator for therapeutic bismuth radioisotopes†
Abstract
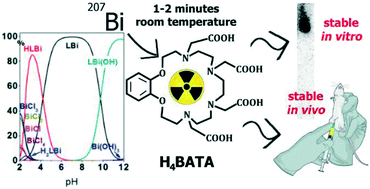
A new benzoazacrown ligand H4BATA was synthesized and its complexation ability towards bismuth cations was evaluated. Binding of cation occurs at room temperature in a few minutes and formed complex exhibits the same level of inertness as highly stable complex with the well-known H4DOTA in biologically relevant and challenging media under in vivo conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...