The synthesis and biological evaluation of novel gardenamide A derivatives as multifunctional neuroprotective agents†
Abstract
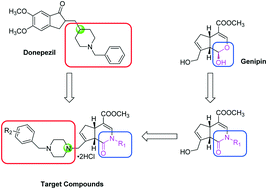
A novel series of gardenamide A derivatives was synthesized as potential anti-Alzheimer's disease agents. The neuroprotective effects of these multifunctional agents against oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced neurotoxicity in rat cortical neurons, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)- and amyloid-β1–42 (Aβ1–42)-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons were evaluated. In vitro studies revealed that these compounds demonstrated moderate to good multifunctional neuroprotective activity. Among the entire series, compounds 10e, 10j, 10n and 10p appeared to be the most active multifunctional neuroprotective agents. Studies indicate that compounds 10e, 10f, 10h, 10i, 10j, 10n and 10p exhibit significant activities against OGD-induced neurotoxicity in rat cortical neurons, and 10e, 10j, 10n and 10p show prominent activities against H2O2- and Aβ1–42-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons. Moreover, these derivatives did not exert conspicuous neurotoxicity in rat cortical neurons. Thus, the present study evidently shows that 10e, 10j, 10n and 10p are potent multifunctional neuroprotective agents, which may serve as promising lead candidates for anti-Alzheimer's disease drug development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...