Prospective treatment of Parkinson's disease by a siRNA–LDH nanoconjugate
Abstract
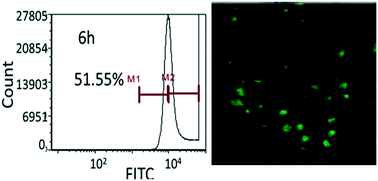
In the world, among the neurodegenerative diseases, Parkinson's is the second most common disease. Although several medications are available in the market, this disease still remains incurable and only the symptoms are controlled to a certain extent with severe side effects. For these reasons we decided to search for a novel therapeutic measure. The objective of this publication was to find a therapeutic procedure to cure this devastating disease. In this study, a biocompatible, easily permeable, cationic nanoparticle-layered double hydroxide was synthesized. Within the layers of these nanoparticles we intercalated α synuclein siRNA, which helps to silence the α synuclein gene. After the intercalation, which was optimized at a 1 : 40 ratio of siRNA : (LDH), we studied its stability in blood by a RNase protection test and serum protection assay. Both proved that LDH was an excellent nanocarrier that can protect intercalated molecules within its layers. After that, several cellular studies were performed by FACS to evaluate its biocompatibility after intercalation and cellular internalization. Results of the biocompatibility studies found it to be nontoxic and in the cellular internalization study, 51.55% of cells were taken into the nanoconjugate and confocal microscopy supported the data from FACS. Lastly, ELISA was performed to discover protein levels in the control, overexpressed, and treated groups of the SH-SY5Y cell line. These results verified that this nanoconjugate is a protective treatment procedure for Parkinson's disease.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...