Synthesis, biological evaluation, and structure activity relationship (SAR) study of pyrrolidine amide derivatives as N-acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA) inhibitors†
Abstract
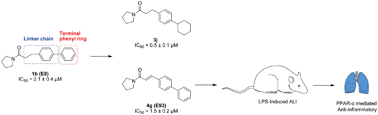
N-Acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA) is one of the key enzymes involved in the degradation of fatty acid ethanolamides (FAEs), especially for palmitoylethanolamide (PEA). Pharmacological blockage of NAAA restores PEA levels, providing therapeutic benefits in the management of inflammation and pain. In the current work, we showed the structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies for pyrrolidine amide derivatives as NAAA inhibitors. A series of aromatic replacements or substituents for the terminal phenyl group of pyrrolidine amides were examined. SAR data showed that small lipophilic 3-phenyl substituents were preferable for optimal potency. The conformationally flexible linkers increased the inhibitory potency of pyrrolidine amide derivatives but reduced their selectivity toward fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). The conformationally restricted linkers did not enhance the inhibitor potency toward NAAA but improved the selectivity over FAAH. Several low micromolar potent NAAA inhibitors were developed, including 4g bearing a rigid 4-phenylcinnamoyl group. Dialysis and kinetic analysis suggested that 4g inhibited NAAA via a competitive and reversible mechanism. Furthermore, 4g showed high anti-inflammatory activities in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced acute lung injury (ALI) model, and this effect was blocked by pre-treatment with the PPAR-α antagonist MK886. We anticipate that 4g (E93) will enable a new agent to treat inflammation and related diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...