Rapid liquid biopsy for Mohs surgery: rare target cell separation from surgical margin lavage fluid with a high recovery rate and selectivity
Abstract
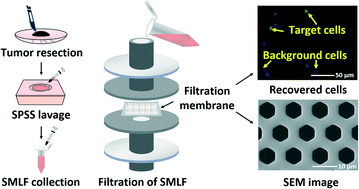
In melanoma surgery, it is difficult to identify residual scattered tumor cells at the surgical margin because of invasive growth. Mohs surgery, widely applied to increase the cure rate and decrease the recurrence rate of melanoma, involves examination of the tissue for tumor cells after tissue removal. Here, we established a liquid biopsy platform for rapid (<5 h), sensitive examination of residual tumor cells at the margin after Mohs surgery using clinical samples from patients with pigment nevus for a demonstration. The design involved highly sensitive, selective rare target cell separation from surgical margin lavage fluid (SMLF) through micropore-arrayed filtration. High recovery rates (86.7% ± 16.3% and 72.7% ± 46.7%, respectively) for separation of spiked 5 A375s (cultured human melanoma cells) and 1 A375 from 1 mL PBS were achieved for this platform. Detection of SMLF samples from patients with pigment nevus was performed, and many (66-7420) Melan-A-positive target cells were successfully recovered and identified, demonstrating the application performance of this rapid liquid biopsy for Mohs surgery in clinical practice. Moreover, a high-selectivity separation of larger target A375 cells from smaller background Jurkat cells was achieved with a high enrichment factor (4.2 ± 1.1). In clinical practice, high selectivity contributes to effective depletion of red blood cells (RBCs), thus ensuring verification of target cells from samples with severe RBC contamination. Furthermore, target cells were obtained with high purity (2.7–35.2%). The capability of this method for rare-cell separation with a high recovery rate and good selectivity may facilitate improvement of performance of Mohs surgery for real clinical practice, including shortening examination time and increasing detection sensitivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...