Accurate modelling of small-scale linear ion trap operating mode using He buffer gas to improve sensitivity and resolution for in-the-field mass spectrometry
Abstract
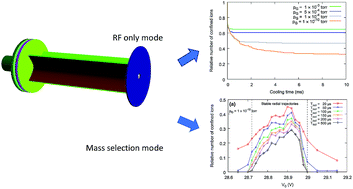
Spectral peak separations of 4 m/z were previously measured using a small-scale mass spectrometer. In this paper the use of He buffer gas during mass analysis was investigated in order to obtain better peak separations (1 m/z) and to optimize the design prior to construction of a new linear ion trap (LIT) device with a novel electrode arrangement and operating mode. Ion/neutral collisions were simulated during LIT operation with an event driven statistical collision treatment tool using 3D electric field boundary element modelling software. Using He buffer gas during the LIT cooling step and assuming a collision-free isolation step during the LIT operating mode, 1 m/z separation can be obtained with also an increased instrument sensitivity. This requires adaptation of both the LIT operating mode and the LIT device configuration. These performance improvements come at the expense of an increase in the analysis duration time which however remains acceptable.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...