Combining X-ray Kβ1,3, valence-to-core, and X-ray Raman spectroscopy for studying Earth materials at high pressure and temperature: the case of siderite
Abstract
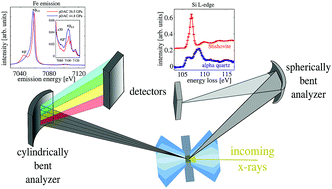
X-ray emission and X-ray Raman scattering spectroscopy are powerful tools to investigate the local electronic and atomic structure of high and low Z elements in situ. Notably, these methods can be applied for in situ spectroscopy at high pressure and high temperature using resistively or laser-heated diamond anvil cells in order to achieve thermodynamic conditions which appear in the Earth's interior. We present a setup for combined X-ray emission and X-ray Raman scattering studies at beamline P01 of PETRA III using a portable wavelength-dispersive von Hamos spectrometer together with the permanently installed multiple-analyzer Johann-type spectrometer. The capabilities of this setup are exemplified by investigating the iron spin crossover of siderite FeCO3 up to 49.3 GPa by measuring the Fe M2,3-edge and the Fe Kβ1,3 emission line simultaneously. With this setup, the Fe valence-to-core emission can be detected together with the Kβ1,3 emission line providing complementary information on the sample's electronic structure. By implementing a laser-heating device, we demonstrate the strength of using a von Hamos type spectrometer for spin state mapping at extreme conditions. Finally, we give different examples of low Z elements' absorption edges relevant for application in geoscience that are accessible with the Johann-type XRS spectrometer. With this setup new insights into the spin transition and compression mechanisms of Earth's mantle materials can be obtained of importance for comprehension of the macroscopic physical and chemical properties of the Earth's interior.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...