Visible-light-induced metal and reagent-free oxidative coupling of sp2 C–H bonds with organo-dichalcogenides: synthesis of 3-organochalcogenyl indoles†
Abstract
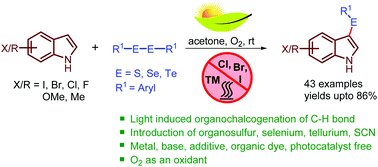
Here, a unique visible-light-induced method for the organochalcogenation of the sp2 C–H bonds of indoles and aniline has been presented using diaryl dichalcogenides (S, Se, and Te) and oxygen as an oxidant avoiding a photocatalyst, base, catalyst, and reagent in acetone at room temperature. This benign protocol allows one to access a wide range of 3-arylselenylindoles, 3-arylthioindoles and even 3-aryltelluroindoles with good to excellent yields. Various functionalities namely, methoxy, and halo either on indoles or aryl dichalcogenides showed amenability to the developed reaction. Furthermore, thiocyanation of the sp2 C–H bonds of indoles has been accomplished by this visible light induced method. A mechanistic understanding by UV-visible, EPR spectroscopy, and cyclic voltammetry suggests that light induces electron transfer from the electron rich arene to oxygen providing an arene radical cation and a superoxide radical anion. Subsequently, reaction of the radical cation with aryl dichalcogenides provides a diaryl chalcogenyl cation which upon removal of protons gave unsymmetrical 3-indolyl aryl chalcogenides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...