In situ preparation of a Nb–Pb codoped and Pd loaded TiO2 photocatalyst from waste multi-layer ceramic capacitors by a chlorination–leaching process†
Abstract
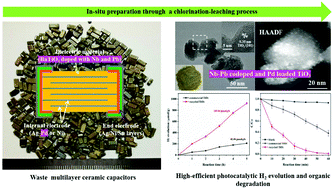
Waste multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), widely existing in discarded appliances, are a valuable resource containing Ti, Nb, Ag, Pd, etc. Based on the principles of waste utilization, low-cost preparation and environmental protection, we in situ prepared a Nb–Pb codoped and Pd loaded TiO2 photocatalyst from waste MLCCs by a simple chlorination–leaching process. The particle sizes of Nb–Pb codoped TiO2 and Pd loading were 50–80 and less than 5 nm, respectively. The visible light absorption of the recycled TiO2 was enhanced and the bandgap was about 2.8 eV. The simulated sunlight photocatalytic H2 production rate and RhB degradation rate of the recycled sample could reach 185.04 μmol g−1 h−1 and 0.078 min−1, respectively, which were 4.4 and 5 times higher than those of commercial TiO2. The recycled sample exhibited excellent photostability and reusability. The highly efficient photocatalytic performance was attributed to the Nb–Pb codoping and Pd loading, which enhanced the visible light absorption and efficient charge separation. Moreover, DFT calculations suggested that the Nb–Pb codoping introduced the impurity levels into the bandgap, which decreased the photon energy required for electron transition and thus enhanced the visible light absorption. The Pd loading received the excited electrons and improved the charge separation. This study provides a novel and sustainable process to convert e-waste into a highly efficient photocatalyst, delivering environmental benefits.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...