Perigestational high folic acid: impact on offspring's peripheral metabolic response
Abstract
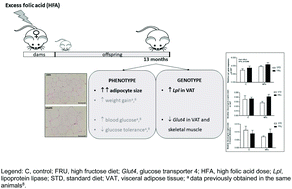
Offspring of dams exposed to excess folic acid during the perigestational period have been shown by us to be predisposed to metabolic dysfunction revealed by hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, increased insulin and decreased adiponectin in late adulthood. This work aims to characterize adipocyte phenotype and expression profile of genes in the regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism in visceral adipose tissue and in skeletal muscle. From mating until weaning, a recommended dose of folic acid for pregnancy (C, 2 mg of folic acid per kg of diet) or a high folic acid dose (HFA, 40 mg of folic acid per kg of diet) was administered to Sprague-Dawley females. At 10 months of age progeny were divided into groups fed the standard chow (C/STD and HFA/STD) and groups fed the standard chow plus drinking water with 10% fructose (C/FRU and HFA/FRU), as an additional metabolic challenge. Adipocyte morphology and quantification of key genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism were studied in visceral adipose tissue and skeletal muscle of 13 months old offspring. HFA exposure led to an enlargement of visceral adipose cells most likely mediated by an upregulation of lipoprotein lipase, and it tended to downregulate Glut4 in visceral adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. Fructose exposure in a background of perigestational excess folic acid, but not in controls, induced an upregulation of lipogenesis pathway genes and it decreased jejunal expression of the proton-coupled folate transporter (Pcft1). In addition, fructose exposure led to a downregulation of jejunal Sglt1 in control animals. Our data suggest that high folic acid exposure during the perigestational period caused morphologic and genic alterations related to insulin resistant states indicating that this intervention may act as an effective programmer of long-term metabolic dysfunction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...