Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis strain CCFM687 regulated emotional behavior and the central BDNF pathway in chronic stress-induced depressive mice through reshaping the gut microbiota†
Abstract
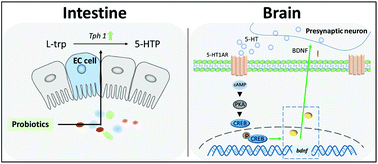
Increasing evidence points to the effect of the gut microbiota on central nervous system functions. Supplementation of certain microbial strains has been demonstrated to alleviate depressive behaviors and neurological abnormalities. This study took the approach to screen for an anti-depressive Bifidobacterium longum strain from fourteen candidates and systematically verified its effect in a chronic stress-induced depression mice model. B. longum subsp. infantis strain CCFM687 could significantly enhance the biosynthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HTP) in vitro in RIN14B cells through up-regulation of the Tph1 gene expression. Administration of CCFM687 in mice significantly improved the scores in behavioral tests and increased the level of 5-HTP and serotonin (5-HT) in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of the brain. The brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the PFC was also increased, possibly through the 5-HT1A-CREB-BDNF pathway. In addition, CCFM687 alleviated the hyperactivity of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis response and accordingly reversed the peripheral inflammation status. Moreover, the stress-induced structural and functional dysbiosis of the gut microbiome was improved by CCFM687, through increased alpha diversity and abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria, in conjunction with inhibition of pathogenic gene expression. In summary, these results indicate that supplementation of B. longum subsp. infantis strain CCFM687 may prevent the onset of depression from chronic stress, and RIN14B could serve as an efficient cell model for rapid screening of anti-depressive probiotics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...