Urolithin A targets the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathways and prevents IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis: in vitro and in vivo studies
Abstract
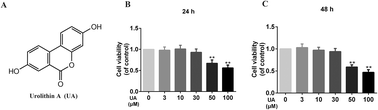
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease, whose progression is closely related to the inflammatory environment. Urolithin A (UA), a natural metabolite of a class of compounds (ellagitannins and ellagic acid) found in pomegranates and other fruits and nuts, has been proved to exert anti-inflammatory effects in a variety of diseases. However, the exact role of UA in OA development is still unclear. In the present study, we examined the latent mechanism of UA and its protective role in the progression of OA by both in vitro and in vivo experiments. In vitro, UA inhibited the interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) induced over-production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in a concentration-dependent manner in human OA chondrocytes. Furthermore, by downregulating the expression of metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) and thrombospondin motifs 5 (ADAMTS5), UA attenuated the degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) induced by IL-1β. Mechanistically, UA was found to suppress the activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathways. In vivo, in a surgically induced mouse OA model, UA-induced protective effects in OA development could be detected. In summary, this research suggested that UA may be adopted as a new therapeutic agent for the treatment of OA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...