Alginate oligosaccharide (AOS) improves immuno-metabolic systems by inhibiting STOML2 overexpression in high-fat-diet-induced obese zebrafish†
Abstract
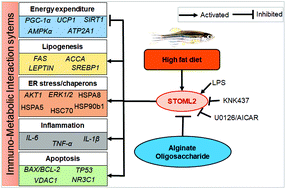
This study aimed to evaluate the potentially beneficial effects of alginate oligosaccharide (AOS) on the modulation of immuno-metabolic pathways in high-fat-diet (HFD)-induced obese zebrafish and the underlying mechanism. AOS showed a marked anti-obesity effect in that it reduced body weight, BMI, and the blood glucose level. To understand the mechanisms of action of AOS, comparative proteomics was performed through UPLC-HDMSE analysis between HFD vs. normal diet (NFD) and HFD + AOS vs. HFD. Among 146 proteins differentially modulated by AOS in HFD-induced obesity zebrafish, STOML2 (Stomatin-like protein 2) was selected as a specific biomarker. AOS suppressed obesity and pathophysiological disorders in HFD-fed zebrafish by modulating lipid metabolism, suppressing inflammation, downregulating apoptosis-related genes, and improving immune function by inhibiting STOML2. Our results suggest that STOML2 can serve as a platform for further studies to discover novel treatments for metabolic disorders. AOS might be useful as a dietary health supplement, especially for reducing obesity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...