Epicatechin influences primary hemostasis, coagulation and fibrinolysis
Abstract
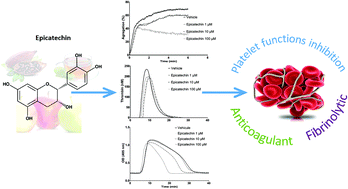
The different stages of hemostasis (i.e., primary hemostasis, coagulation and fibrinolysis) are involved in the early atherothrombosis steps. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of epicatechin, a major flavonoid compound, on the hemostasis phenotype using clinically relevant in vitro global assays that mimic the complexity of the in vivo hemostasis systems. Plasma samples from 10 healthy volunteers were spiked with increasing concentrations of epicatechin (1 to 100 μM). Epicatechin effect on primary hemostasis, coagulation and fibrinolysis was assessed by measuring platelet aggregation using light transmission aggregometry, thrombin generation and clot lysis time (CLT), respectively. Epicatechin (100 μM) significantly decreased the maximal platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate (−39%), thrombin receptor activating peptide (−48%), epinephrine (−30%), and collagen (−30%). The endogenous thrombin potential was significantly reduced starting from 1 μM epicatechin (1332 ± 230 versus 1548 ± 241 nM min for control) (p < 0.01). Fibrinolysis was promoted by epicatechin, as indicated by CLT decrease by 16 and 33% with 10 and 100 μM epicatechin respectively, compared with control (1271 ± 775 s). These findings show that epicatechin reduces platelet function and leads to an anticoagulant and pro-fibrinolytic profile, providing new evidence of its interest for cardiovascular disease prevention.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...