Urinary and plasmatic metabolomics strategy to explore the holistic mechanism of lignans in S. chinensis in treating Alzheimer's disease using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS†
Abstract
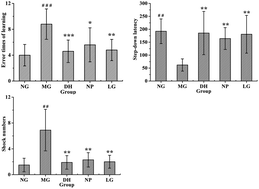
Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill (S. chinensis), a functional food, is used as a tonic and sedative agent in traditional Chinese medicine. Modern pharmacological research has proved that S. chinensis could prevent and treat age-related neurodegenerative diseases. The presence of bioactive lignans in S. chinensis is the main reason for its neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement effects. This study aimed to clarify the mechanism of lignans in S. chinensis in ameliorating learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease (AD) animals. The step-down test and Morris water maze (MWM) test were used to verify the effects of lignans in S. chinensis on learning and memory in AD animals. Then, metabolomics approaches based on ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) were used to clarify the mechanism of lignans in S. chinensis in treating AD. Finally, quantitative analysis of AD-related neurotransmitters in the brain was conducted after treatment with lignans in S. chinensis. In the MWM and step-down tests, lignans in S. chinensis showed a clear ability to ameliorate the impaired learning and memory of AD animals. A total of 31 endogenous metabolites were identified after treatment with lignans in S. chinensis, which were associated with lignans ameliorating learning and memory. These biomarkers were mainly associated with polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism and amino acid and vitamin metabolism. Moreover, lignans in S. chinensis upregulated the levels of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), acetylcholine (Ach), norepinephrine (NE) and glycine (Gly) and downregulate the level of aspartic acid (Asp). Lignans in S. chinensis might alleviate the neurotoxic effects of neurological inflammation and oxidative stress, Aβ deposition, and tau phosphorylation via the regulation of multiple endogenous metabolic pathways during pathological AD. The research might provide useful support for the further study of pharmacology and new drug development of lignans in S. chinensis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...