The fucoidan from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum ameliorates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
Abstract
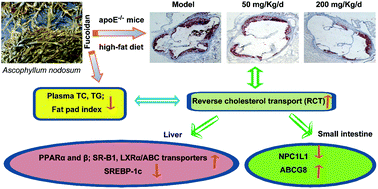
Hyperlipidemia is a major cause of atherosclerosis. Reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) is believed to attenuate hyperlipidemia and the progression of atherosclerosis. Although fucoidans are reported to have hypolipidemic effects, the underlying mechanisms are unclear. Furthermore, few reports have revealed the anti-atherosclerotic effects and the underlying mechanisms of fucoidans. This study was designed to investigate the anti-atherosclerotic effect and mechanisms of the fucoidan from seaweed A. nodosum. Our results demonstrated that the fucoidan administration ameliorated atherosclerotic lesion and lipid profiles in a dose-dependent manner in the apolipoprotein E-deficient (apoE−/−) mice fed a high-fat diet. In the apoE−/− mice liver, the fucoidan treatment significantly increased the expression of scavenger receptor B type 1 (SR-B1), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α and β, liver X receptor (LXR) α, ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) A1 and ABCG8; and markedly decreased the expression of PPARγ and sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) 1c, but not low-density lipoprotein receptor, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase A1, LXRβ and ABCG1. In the small intestine of the apoE−/− mice, the fucoidan treatment significantly reduced the expression of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) and dramatically improved ABCG8 levels. These results demonstrated for the first time that the fucoidan from A. nodosum attenuated atherosclerosis by regulating RCT-related genes and proteins expression in apoE−/− mice. In summary, this fucoidan from A. nodosum may be explored as a potential compound for prevention or treatment of hyperlipidemia-induced atherosclerosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...