Chia seeds: an ancient grain trending in modern human diets
Abstract
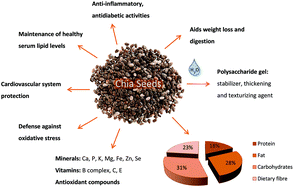
Currently, in order to ensure adequate intake of nutrients to complement the normal diet, the consumption of seeds such as Salvia hispanica L. (commonly known as chia seeds) is increasing. For this reason, investigations concerning the composition and potential health effects of chia seeds are being carried out. Moreover, the recent approval of chia seeds as a Novel Food by the European Parliament allows its consumption and incorporation in a wide range of foods; thus, they have become widely available. Concerning their nutritional aspects, chia seeds are an excellent source of fat (20% to 34%), particularly polyunsaturated fatty acids such as α-linolenic (60%) and linoleic (20%) acids. Moreover, high levels of protein (16% to 26%), mainly prolamins, and dietary fibre contents (23% to 41%) have been reported. Vitamins (mostly B complex) and minerals (calcium, phosphorus, and potassium, among others) have also been described in appreciable amounts. Additionally, due to the absence of gluten, these seeds are appropriate for coeliac patients. Regarding other bioactive compounds, chia seeds are also a source of antioxidants, such as chlorogenic and caffeic acids, quercetin and kaempferol. Due to their described composition, chia seeds have been related to different medicinal effects, particularly anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic activities and positive effects on cardiovascular disease and hypertension. The aim of this paper is to perform a systematic review of chia seeds to provide an update of the knowledge about their morphology, nutritional and chemical composition, possible human health benefits and role as a functional food.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...