Hydroxy-α-sanshool isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum attenuates learning and memory impairments in scopolamine-treated mice
Abstract
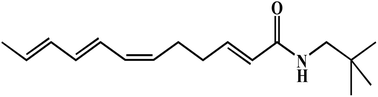
Learning and memory impairments are common symptoms of dementia in neurodegenerative disorders. Occasionally, we found that Zanthoxylum bungeanum pericarps (ZBP) significantly activated the spontaneous activity of the hippocampus (HIPP) and paraHIPP (P < 0.001, uncorrected), implying the potential ability of ZBP to improve cognitive impairments. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the improving effect of hydroxy-α-sanshool (HAS), a characteristic ingredient of ZBP, against scopolamine (1 mg kg−1, i.p.)-induced learning and memory deficits. HAS (5 mg kg−1, p.o.) markedly reversed scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments, as indicated by its performance in the passive avoidance test and Morris water maze test (P < 0.01). Furthermore, HAS (2.5 and 5.0 mg kg−1, p.o.) also dose-dependently prevented changes in hippocampal neuronal morphology and apoptosis, inhibited acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, increased the acetylcholine (ACh) content, and increased the protein and mRNA expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and phospho-cAMP response element-binding (p-CREB) compared with those in the model group (P < 0.05 & P < 0.01). These findings demonstrated that HAS attenuated scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments mainly by enhancing the activity of the cholinergic system and increasing the CREB/BDNF signalling pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...